Introduction
In the intricate world of automotive transmissions, the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission stands out for its reliability and performance. This advanced transmission system, employed in a range of vehicles, leverages solenoids to manage gear shifts and ensure smooth operation. When problems arise within this system, understanding solenoids and their role becomes crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoid diagram, offering insights into its function, types, troubleshooting, and maintenance. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or an enthusiastic DIYer, this tutorial will equip you with the knowledge needed to keep your vehicle running optimally.
Explanation of Solenoids and Their Function in the Transmission
Solenoids are pivotal components in automatic transmissions like the ZF 6HP Generation 2. These electromechanical devices are responsible for controlling hydraulic fluid flow within the transmission, which directly affects gear shifts and overall performance.
When electrical current flows through a solenoid coil, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field, in turn, engages or disengages specific transmission components, allowing precise control over power transfer from the engine to the wheels. Essentially, solenoids act as valves that manage hydraulic pressure, ensuring smooth transitions between gears. Without properly functioning solenoids, shifting would be erratic and unpredictable, leading to a less enjoyable driving experience.
Types of Solenoids Used in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Transmission
The ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission employs several types of solenoids, each playing a critical role in its operation. Here’s a closer look at the main types:
- Pressure Control Solenoid: This solenoid regulates hydraulic pressure within the transmission. It adjusts in real-time based on engine load and speed, ensuring smooth gear shifts and optimal performance.
- Shift Solenoid: Responsible for enabling gear changes, the shift solenoid controls the engagement of clutches and brakes. Its precise operation allows for seamless transitions, contributing to a comfortable driving experience.
- Torque Converter Lock-Up Solenoid: This solenoid optimizes efficiency during highway driving by locking the torque converter at specific speeds. This not only improves fuel economy but also reduces engine strain.
Understanding these solenoids and their functions is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring the transmission system performs at its best.
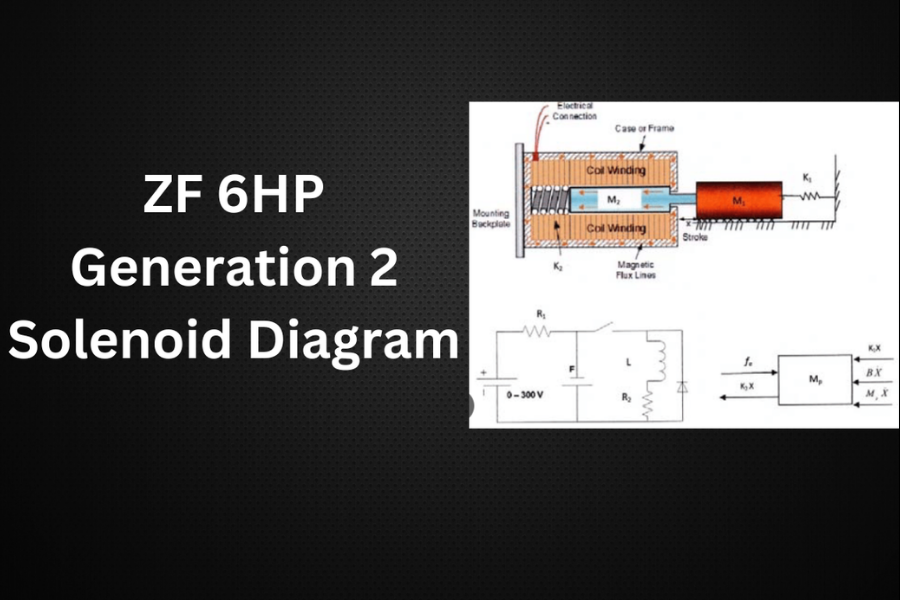
How to Read and Understand a Solenoid Diagram for the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Transmission
Interpreting a solenoid diagram for the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission can initially seem overwhelming. However, with a bit of guidance, it becomes more manageable. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Identify Key Components: Begin by locating the solenoids on the diagram. These are usually labeled with their functions, such as “shift,” “pressure,” or “lockup” solenoids. Understanding what each solenoid does is crucial for diagnosing issues.
- Examine Wiring Connections: Lines on the diagram represent electrical pathways. Trace these lines to understand how power flows through each solenoid. This information is vital for troubleshooting electrical issues.
- Look for Color Coding: Diagrams often use color coding to denote different functions or operational states of the solenoids. Pay close attention to these details as they provide additional context.
- Refer to the Legend or Notes: Many diagrams come with a legend or additional notes. These explanations can help clarify the symbols and connections used in the diagram, making it easier to understand and troubleshoot.
By familiarizing yourself with these elements, you’ll be better equipped to interpret solenoid diagrams and diagnose any issues with the transmission system.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Solenoids in This Transmission
When solenoids in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission malfunction, several symptoms may arise. Recognizing these signs is essential for timely intervention:
- Delayed Shifting: If you notice a delay in gear changes, it could be a sign of a solenoid issue. This delay can stem from a malfunctioning solenoid that is not properly regulating hydraulic pressure.
- Erratic or Harsh Gear Shifts: A vehicle that feels like it’s slamming into gears may have a faulty solenoid. This issue often results from improper hydraulic pressure management.
- Warning Lights: Dashboard warning lights related to transmission performance should not be ignored. These lights can indicate problems with solenoids or other transmission components.
- Unusual Sounds: Whining or grinding noises during operation can signal solenoid issues. These sounds often indicate problems with fluid flow or solenoid engagement.
- Diagnostic Codes: Using an OBD-II scanner to check for error codes can pinpoint specific issues with the solenoids. This tool can provide valuable information for troubleshooting and repair.
By being aware of these symptoms and utilizing diagnostic tools, you can address solenoid issues promptly and prevent further damage to the transmission system.
Tips for Maintaining and Replacing Solenoids in the ZF 6HP Generation 2
Proper maintenance and timely replacement of solenoids are key to ensuring the longevity and performance of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission. Here are some tips to consider:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct periodic checks of the solenoids to identify signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks. Early detection of issues can prevent more significant problems down the line.
- Use OEM Parts: When replacing solenoids, always opt for original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts. These components ensure compatibility and reliability within the transmission system.
- Clean Installation Area: Before installing a new solenoid, clean the area thoroughly to remove any debris. This step helps prevent contamination that could affect the solenoid’s performance.
- Follow Torque Specifications: Adhere to the manufacturer’s torque specifications during reassembly. Over-tightening can cause damage, while under-tightening may lead to fluid leaks.
- Monitor Performance: After replacing a solenoid, observe the transmission’s performance closely. Any unusual behavior should be addressed immediately to prevent further issues.
- Seek Professional Help: If you’re unsure about performing maintenance or repairs yourself, consider consulting a professional. Expert assistance can be invaluable when dealing with complex components like solenoids.
By following these maintenance tips, you can extend the lifespan of your solenoids and ensure smooth operation of the transmission system.
Conclusion
The ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission is a sophisticated system that relies on solenoids for optimal performance. Understanding the role of these components, how to read solenoid diagrams, and how to troubleshoot common issues are essential for maintaining and repairing this transmission system.
Solenoids are crucial for controlling hydraulic fluid flow, which directly impacts gear shifts and overall vehicle performance. Familiarizing yourself with the types of solenoids and their functions, as well as learning how to interpret solenoid diagrams, will enhance your ability to diagnose and address issues effectively.
Regular maintenance, timely replacement, and professional guidance when needed are key to keeping the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission running smoothly. By staying informed and proactive, you can ensure that your vehicle remains in top condition, providing a reliable and enjoyable driving experience.